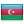
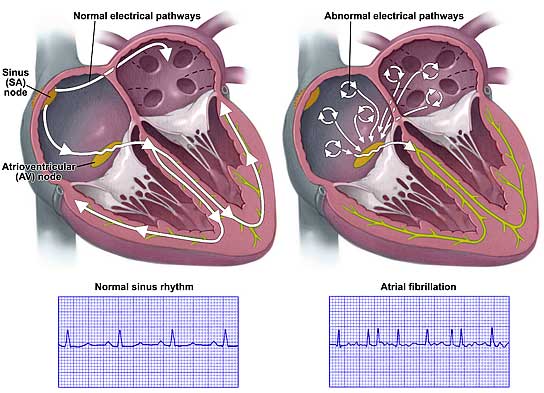
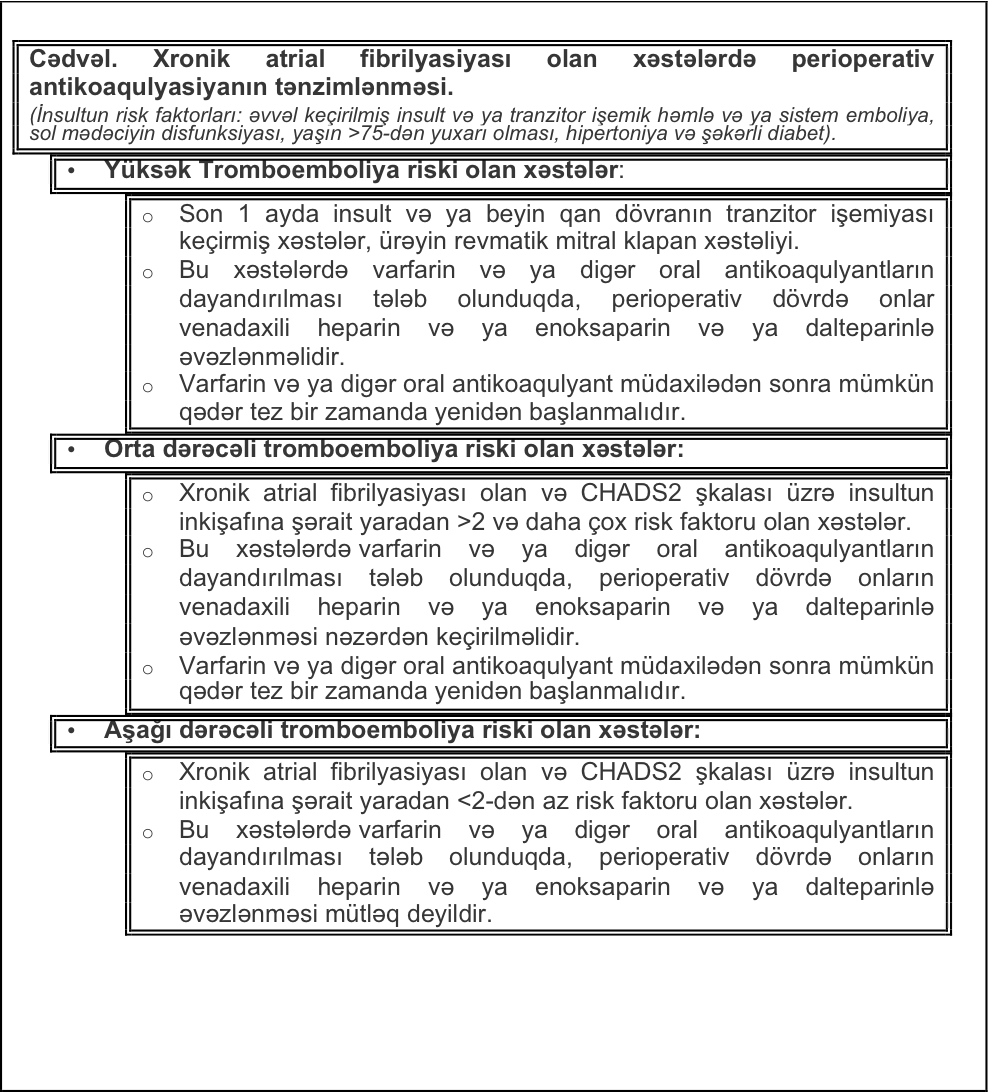
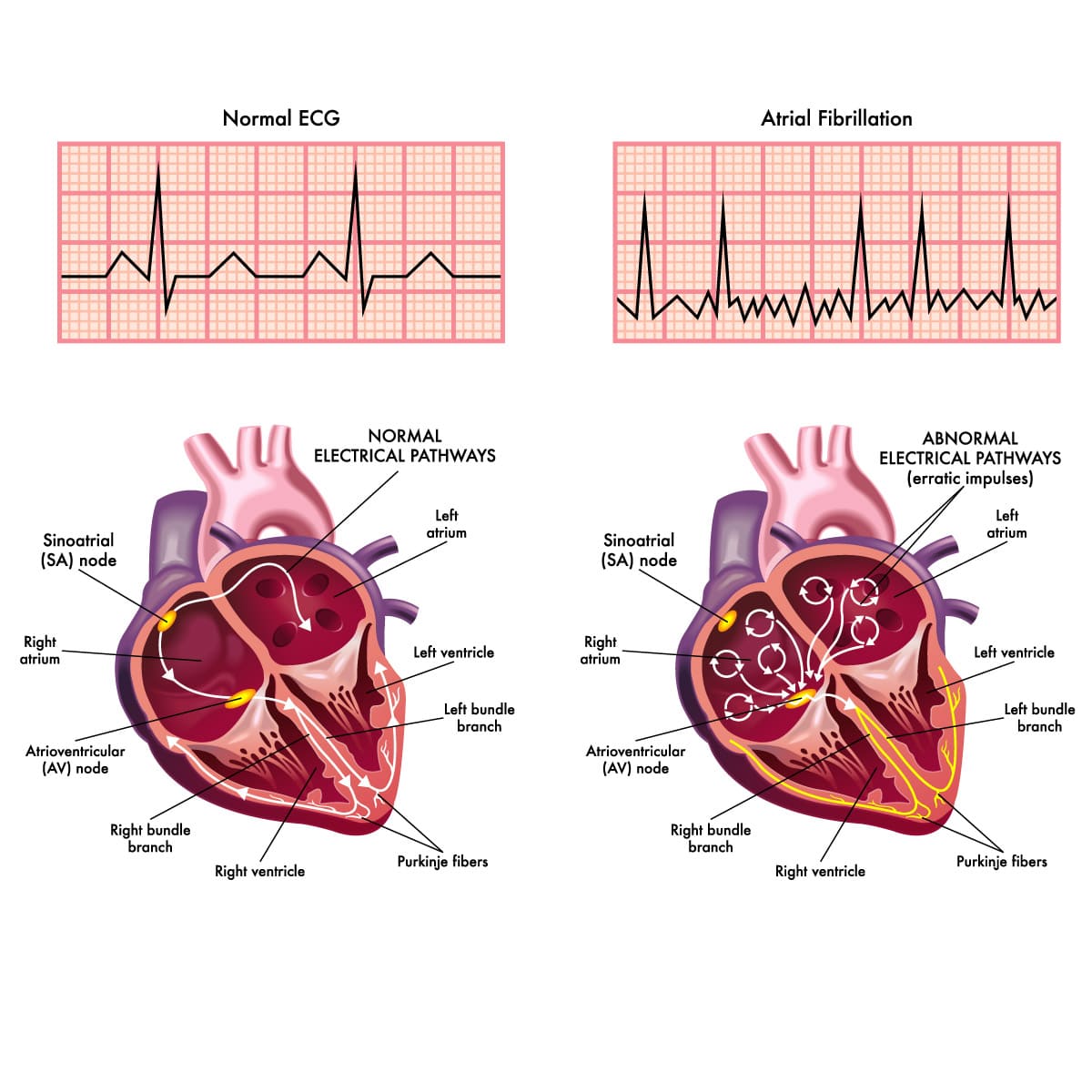
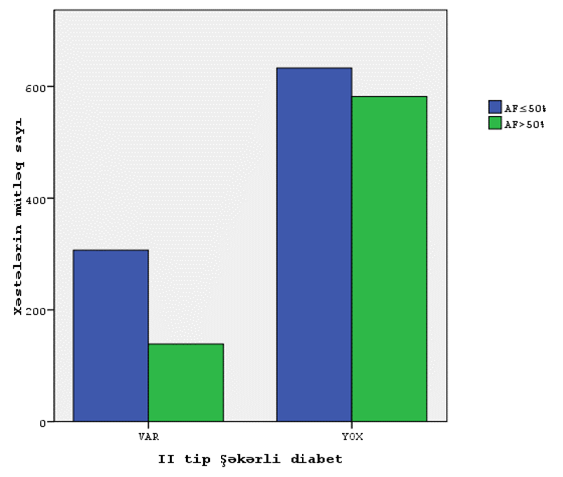
The article discusses structural remodeling and atrial fibrosis in the development of atrial fibrillation (AF).AF occurs most often due to risk factors such as coronary heart disease ,arterial hypertension ,cardiac insufficiency ,mitral vale malformations and extracardiac cause. Special attention is given to the assessment of the function of the left atrium (LA), its enlargement and deformities ,playing crucial role in depression of LA pumping function. It is noted that expansion of LA cavity with the increase in myocardial fibrosis plays a key role in the occurrence of AF.The lectins family protein-galectin 3, playing a special role in development of atrial fibrosis is a powerful factor of activation of fibroblasts and synthesis of collagen ,participating in the development of myocardial fibrosis . Further, the article indicates the consequences of the activation of renin -angiotensin -aldosterone system and other neurohumoral factors like TGF-β1 and osteopontin involved in the development of fibrosis of myocardium and cardiac heart failure. It was demonstrated that aldosterone regulates the production of fibro genic factors and promotes activation of fibroblasts. Thus, understanding of the mechanisms and finding of markers of myocardial fibrosis and predictors of AF development will allow timely elimination of AF risk group and prevention of this arrhythmias.
AZERBAIJAN CARDIOLOGY JOURNAL
- Articles Popular ArticlesLatest Articles
- Characterıstıcs of cardiovascular activity in multipyrium women with iron deficiency anemiaGeneral cardiology
- TAVR as treatment of choice in severe aortic regurgitation with multivalve pathology and chronic kidney disease patientHeart valvular diseases
- The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Assessing Quality of Life in Patients with Arrhythmia Who Underwent Breast Cancer SurgeryGeneral cardiology
- Current issue
- Archives
- About Us
- Editorial
- Photo
- Videos
- News